In the dynamic landscape of modern business, efficient management and seamless integration of various operational facets are crucial for sustained growth and competitive advantage.
This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play, acting as the central nervous system for organizations of all sizes.
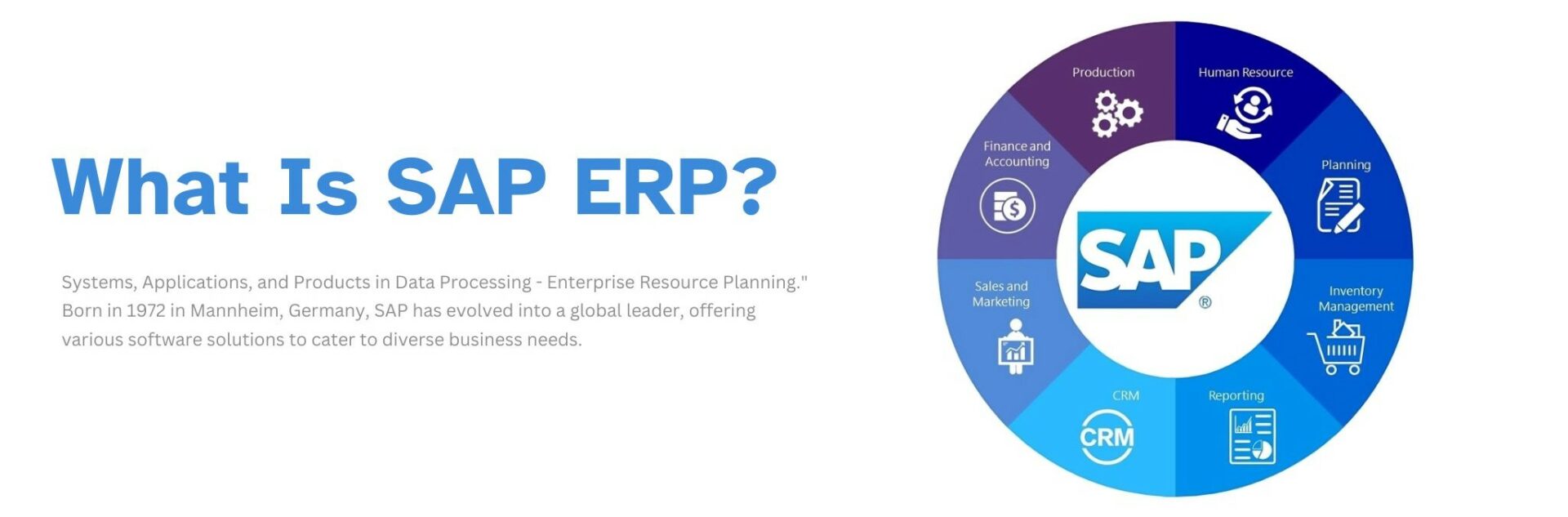
Among the leading ERP solutions, SAP ERP stands out as a comprehensive and widely adopted platform. But what exactly *is* SAP ERP? This article delves deep into the intricacies of SAP ERP, exploring its core functionalities, benefits, modules, implementation considerations, and its role in the contemporary business environment.
Understanding the Fundamentals of ERP
Before dissecting SAP ERP specifically, it’s essential to grasp the underlying concept of ERP itself. At its core, ERP is an integrated software solution that manages and automates various business processes across different departments within an organization. Imagine a company where sales, finance, manufacturing, human resources, and supply chain operate in silos, using disparate systems and spreadsheets. This can lead to data inconsistencies, communication breakdowns, and inefficiencies. ERP addresses these challenges by providing a centralized database and a unified platform where all these functions can seamlessly interact and share information.
Think of ERP as a digital backbone that connects all the critical departments of a business. It eliminates data silos, streamlines workflows, automates repetitive tasks, and provides real-time visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs). By integrating various business functions, ERP enables organizations to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance overall performance. ERP systems are designed to support a wide range of business processes, including:
- Financial Management: Managing accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources: Handling payroll, employee benefits, and talent management.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizing inventory, procurement, and logistics.
- Manufacturing: Controlling production planning, scheduling, and execution.
- Sales and Marketing: Managing customer relationships, sales orders, and marketing campaigns.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Improving customer interactions and satisfaction.
By centralizing these processes, ERP provides a holistic view of the business, enabling better coordination, improved decision-making, and enhanced overall efficiency. Furthermore, modern ERP systems often incorporate advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud computing to further enhance their capabilities and provide even greater value to organizations.
What Makes SAP ERP Unique?
SAP, which stands for Systems, Applications & Products in Data Processing, is a German multinational software corporation that develops enterprise software to manage business operations and customer relations. SAP ERP is their flagship product and one of the most widely used ERP systems globally. What sets SAP ERP apart from other ERP solutions? Several factors contribute to its prominence and reputation:
- Comprehensive Functionality: SAP ERP offers a broad range of modules and functionalities, covering virtually every aspect of business operations. This comprehensive suite allows organizations to manage everything from finance and accounting to supply chain and human resources within a single integrated system.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SAP ERP is designed to scale with the growth of the organization. It can accommodate the needs of small businesses as well as large multinational corporations. Its modular architecture allows organizations to select and implement only the modules they need, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Customization and Configuration: SAP ERP is highly customizable and configurable to meet the specific requirements of different industries and businesses. Organizations can tailor the system to their unique processes and workflows, ensuring that it aligns perfectly with their operational needs.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: SAP offers industry-specific versions of its ERP system, tailored to the unique requirements of various sectors, such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and financial services. These industry-specific solutions include pre-configured processes, best practices, and functionalities designed to address the specific challenges and opportunities within each industry.
- Advanced Technologies: SAP ERP incorporates advanced technologies like AI, ML, and cloud computing to enhance its capabilities and provide greater value to organizations. These technologies enable automation, predictive analytics, and improved decision-making.
- Extensive Ecosystem: SAP has a vast ecosystem of partners, consultants, and developers who provide implementation services, training, and support to organizations using SAP ERP. This ecosystem ensures that organizations have access to the expertise and resources they need to successfully implement and maintain their SAP ERP system.
In essence, SAP ERP is more than just a software system; it’s a comprehensive platform that empowers organizations to optimize their business processes, improve efficiency, and drive growth. Its robust functionality, scalability, customization options, and industry-specific solutions make it a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes and across various industries.
Exploring the Key Modules of SAP ERP
SAP ERP is comprised of various modules, each designed to address specific business functions. These modules can be implemented independently or integrated with each other to create a comprehensive ERP solution. Here’s a closer look at some of the key modules within SAP ERP:
Financial Accounting (FI)
The Financial Accounting (FI) module is the core of SAP ERP, responsible for managing all financial transactions and reporting. It provides a comprehensive suite of functionalities for:
- General Ledger Accounting: Maintaining the general ledger, which is the central repository for all financial transactions.
- Accounts Payable (AP): Managing vendor invoices, payments, and reconciliation.
- Accounts Receivable (AR): Managing customer invoices, payments, and collections.
- Asset Accounting: Tracking and managing fixed assets, including depreciation and amortization.
- Bank Accounting: Managing bank accounts, reconciliations, and electronic payments.
- Financial Reporting: Generating financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
The FI module ensures accurate and timely financial reporting, enabling organizations to comply with regulatory requirements and make informed financial decisions. It integrates seamlessly with other modules, such as Sales and Distribution (SD) and Materials Management (MM), to provide a complete picture of the organization’s financial performance.
Controlling (CO)
The Controlling (CO) module focuses on internal management accounting and cost control. It provides tools and functionalities for:
- Cost Element Accounting: Tracking and analyzing costs by cost element, such as materials, labor, and overhead.
- Cost Center Accounting: Allocating costs to cost centers, such as departments or functional areas.
- Profit Center Accounting: Tracking profitability by profit center, such as product lines or geographic regions.
- Product Costing: Calculating the cost of goods manufactured, including direct materials, direct labor, and overhead.
- Profitability Analysis (CO-PA): Analyzing profitability by market segment, customer, or product.
The CO module provides valuable insights into the organization’s cost structure and profitability, enabling managers to make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, and performance improvement. It integrates with other modules, such as Production Planning (PP) and Materials Management (MM), to provide a comprehensive view of the organization’s cost and profitability performance.
Materials Management (MM)
The Materials Management (MM) module manages the procurement, inventory, and warehousing of materials. It provides functionalities for:
- Purchasing: Managing purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and vendor contracts.
- Inventory Management: Tracking inventory levels, managing stock movements, and performing inventory counts.
- Warehouse Management: Managing warehouse operations, including receiving, putaway, picking, and shipping.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Planning material requirements based on demand and inventory levels.
- Invoice Verification: Matching invoices to purchase orders and goods receipts.
The MM module optimizes the flow of materials throughout the organization, ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time and at the right cost. It reduces inventory costs, improves efficiency, and enhances customer service. It integrates with other modules, such as Production Planning (PP) and Sales and Distribution (SD), to provide a seamless flow of materials throughout the supply chain.
Sales and Distribution (SD)
The Sales and Distribution (SD) module manages the sales process, from order entry to delivery and invoicing. It provides functionalities for:
- Sales Order Management: Creating and managing sales orders, including pricing, discounts, and shipping information.
- Shipping and Delivery: Planning and executing deliveries, including packing, shipping, and transportation.
- Billing: Creating and managing invoices, including pricing, taxes, and payment terms.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Managing customer interactions, tracking sales leads, and providing customer support.
- Sales Reporting: Generating sales reports and analyzing sales performance.
The SD module streamlines the sales process, improves customer service, and increases sales revenue. It integrates with other modules, such as Materials Management (MM) and Financial Accounting (FI), to provide a complete view of the sales cycle.
Production Planning (PP)
The Production Planning (PP) module manages the production process, from planning to execution. It provides functionalities for:
- Demand Management: Forecasting demand for products and services.
- Master Production Scheduling (MPS): Creating a production plan based on demand and capacity.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Planning material requirements based on the production plan.
- Shop Floor Control: Managing production orders, tracking production progress, and collecting production data.
- Capacity Planning: Planning and managing production capacity.
The PP module optimizes the production process, reduces lead times, and improves production efficiency. It integrates with other modules, such as Materials Management (MM) and Controlling (CO), to provide a complete view of the production process and its associated costs.
Human Capital Management (HCM)
The Human Capital Management (HCM) module manages all aspects of human resources, from recruitment to retirement. It provides functionalities for:
- Recruitment: Managing job postings, applications, and interviews.
- Personnel Administration: Managing employee data, such as personal information, job titles, and salary information.
- Payroll: Calculating and processing payroll, including taxes and deductions.
- Benefits Administration: Managing employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
- Talent Management: Managing employee performance, development, and succession planning.
- Time Management: Tracking employee time and attendance.
The HCM module streamlines HR processes, improves employee satisfaction, and ensures compliance with labor laws and regulations. It provides a centralized platform for managing all employee-related information and activities.
These are just some of the key modules within SAP ERP. Depending on the specific needs of the organization, other modules may also be implemented, such as Quality Management (QM), Plant Maintenance (PM), and Project System (PS). The modular architecture of SAP ERP allows organizations to tailor the system to their specific requirements and to implement only the modules they need.
Benefits of Implementing SAP ERP
Implementing SAP ERP can bring numerous benefits to organizations, regardless of their size or industry. These benefits can be broadly categorized into operational efficiency, improved decision-making, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
Operational Efficiency
SAP ERP streamlines business processes, automates repetitive tasks, and eliminates data silos, leading to significant improvements in operational efficiency. Some of the specific benefits include:
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automating tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and report generation reduces manual effort and frees up employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Improved Workflow Efficiency: Streamlining workflows and eliminating bottlenecks improves efficiency and reduces cycle times.
- Reduced Inventory Costs: Optimizing inventory levels and improving inventory management reduces inventory costs and minimizes stockouts.
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: Streamlining the supply chain and improving coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors reduces lead times and improves customer service.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Providing a centralized platform for information sharing and collaboration improves communication and coordination between departments and teams.
By optimizing business processes and automating tasks, SAP ERP enables organizations to do more with less, leading to significant cost savings and improved productivity.
Improved Decision-Making
SAP ERP provides real-time visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs) and provides comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling organizations to make more informed decisions. Some of the specific benefits include:
- Real-Time Data Visibility: Providing real-time access to data across all departments and functions enables managers to make informed decisions based on the latest information.
- Improved Reporting and Analytics: Providing comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities enables organizations to track performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Better Forecasting: Providing tools for demand forecasting and production planning enables organizations to anticipate future needs and to make informed decisions about resource allocation.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Providing tools for risk assessment and mitigation enables organizations to identify and manage potential risks more effectively.
- Improved Compliance: Providing tools for compliance monitoring and reporting enables organizations to comply with regulatory requirements and to avoid penalties.
By providing access to accurate and timely information, SAP ERP empowers organizations to make better decisions, leading to improved performance and competitive advantage.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
SAP ERP enables organizations to provide better customer service, improve customer relationships, and increase customer loyalty. Some of the specific benefits include:
- Improved Order Fulfillment: Streamlining the order fulfillment process and reducing lead times improves customer satisfaction and reduces order cancellations.
- Better Customer Service: Providing customer service representatives with access to customer data and order history enables them to provide more personalized and effective service.
- Improved Communication: Providing tools for customer communication and collaboration enables organizations to build stronger relationships with their customers.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By providing excellent customer service and meeting customer needs, organizations can increase customer loyalty and generate repeat business.
- Personalized Customer Experience: Utilizing CRM functionalities to understand customer preferences and tailor interactions, leading to increased satisfaction.
By focusing on customer needs and providing excellent service, SAP ERP helps organizations build stronger relationships with their customers and to increase customer loyalty.
Increased Profitability
By improving operational efficiency, enabling better decision-making, and enhancing customer satisfaction, SAP ERP ultimately leads to increased profitability. Some of the specific benefits include:
- Reduced Costs: Streamlining business processes and automating tasks reduces costs and improves profitability.
- Increased Revenue: Improving customer service and increasing customer loyalty leads to increased revenue and profitability.
- Improved Margins: Optimizing pricing and reducing costs leads to improved margins and profitability.
- Faster Growth: By improving efficiency and enabling better decision-making, SAP ERP enables organizations to grow faster and more profitably.
- Better Return on Investment (ROI): The combination of cost savings, increased revenue, and improved efficiency leads to a better return on investment for the organization.
In conclusion, the implementation of SAP ERP offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly impact an organization’s success. From streamlining operations and improving decision-making to enhancing customer satisfaction and increasing profitability, SAP ERP provides a comprehensive platform for managing and optimizing business processes.
Considerations for SAP ERP Implementation
Implementing SAP ERP is a complex and challenging undertaking that requires careful planning, execution, and management. Several factors must be considered to ensure a successful implementation. This is not a simple “plug and play” solution; it’s a strategic project with far-reaching implications.
Project Planning and Scope Definition
The first step in implementing SAP ERP is to develop a detailed project plan that outlines the goals, objectives, scope, timeline, and resources required for the implementation. The project plan should clearly define the business processes that will be implemented, the modules that will be used, and the integration points with other systems. A clear scope definition is crucial to avoid scope creep and to ensure that the implementation stays on track.
Data Migration and Cleansing
Migrating data from legacy systems to SAP ERP is a critical and often time-consuming task. The data must be cleansed, validated, and transformed to ensure that it is accurate and consistent. A data migration plan should be developed that outlines the data sources, the data mapping rules, and the data migration procedures. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to serious problems after go-live, so data quality is paramount.
Customization and Configuration
SAP ERP is highly customizable and configurable to meet the specific requirements of different industries and businesses. However, excessive customization can lead to increased costs and complexity. It’s important to carefully evaluate the need for customization and to minimize the amount of customization required. The focus should be on leveraging the standard functionality of SAP ERP as much as possible and only customizing where necessary.
Training and Change Management
Implementing SAP ERP requires significant changes to business processes and work practices. It’s important to provide adequate training to employees so that they can effectively use the new system. A change management plan should be developed to address the organizational and cultural changes that will result from the implementation. Resistance to change can be a major obstacle to a successful implementation, so it’s important to proactively manage the change process and to communicate the benefits of the new system to employees.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Thorough testing and quality assurance are essential to ensure that the SAP ERP system is functioning correctly and that it meets the business requirements. A comprehensive testing plan should be developed that includes unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing. All defects should be documented and resolved before go-live.
Go-Live and Support
The go-live process should be carefully planned and executed to minimize disruption to business operations. A support plan should be developed to provide ongoing support to users after go-live. The support plan should include a help desk, a knowledge base, and a process for resolving issues and addressing user questions. Post-implementation support is crucial for ensuring that users can effectively use the system and that any problems are quickly resolved.
Choosing the Right Implementation Partner
Selecting the right implementation partner is critical to the success of the SAP ERP implementation. The implementation partner should have extensive experience in implementing SAP ERP and a deep understanding of the organization’s industry and business processes. The partner should also have a proven methodology for implementing SAP ERP and a track record of successful implementations. A good implementation partner can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the implementation process.
In summary, a successful SAP ERP implementation requires careful planning, execution, and management. By considering the factors outlined above, organizations can increase their chances of a successful implementation and realize the full benefits of SAP ERP.
SAP ERP in the Cloud vs. On-Premise
One of the key decisions organizations face when implementing SAP ERP is whether to deploy it on-premise or in the cloud. Each deployment model has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the organization.
On-Premise Deployment
In an on-premise deployment, the SAP ERP system is installed and maintained on the organization’s own servers and infrastructure. The organization is responsible for all aspects of the system, including hardware, software, security, and maintenance. This model offers greater control over the system and data, but it also requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Advantages of On-Premise Deployment:
- Greater Control: Organizations have complete control over the system and data.
- Customization: Organizations can customize the system to meet their specific requirements.
- Security: Organizations can implement their own security measures to protect their data.
- Compliance: Organizations can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Disadvantages of On-Premise Deployment:
- High Upfront Costs: Requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: Requires ongoing maintenance costs for hardware, software, and security.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling the system can be difficult and expensive.
- IT Resource Requirements: Requires significant IT resources to manage and maintain the system.
Cloud Deployment
In a cloud deployment, the SAP ERP system is hosted and managed by a third-party cloud provider. The organization accesses the system over the internet and pays a subscription fee for the service. This model offers lower upfront costs and reduced maintenance costs, but it also requires organizations to relinquish some control over the system and data.
Advantages of Cloud Deployment:
- Lower Upfront Costs: Requires lower upfront costs as the infrastructure is provided by the cloud provider.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Reduces maintenance costs as the cloud provider is responsible for maintaining the system.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to meet changing business needs.
- Accessibility: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud provider handles updates and maintenance.
Disadvantages of Cloud Deployment:
- Less Control: Organizations have less control over the system and data.
- Security Concerns: Organizations must rely on the cloud provider to secure their data.
- Customization Limitations: Customization options may be limited.
- Internet Dependency: Requires a reliable internet connection.
- Vendor Lock-in: Can be difficult to switch cloud providers.
The decision of whether to deploy SAP ERP on-premise or in the cloud depends on the specific needs and priorities of the organization. Organizations that prioritize control, customization, and security may prefer an on-premise deployment. Organizations that prioritize lower costs, scalability, and accessibility may prefer a cloud deployment. Hybrid solutions, combining elements of both on-premise and cloud deployments, are also becoming increasingly popular.
The Future of SAP ERP
SAP ERP is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. Several trends are shaping the future of SAP ERP, including:
Cloud Adoption
Cloud adoption is accelerating as organizations increasingly recognize the benefits of cloud computing. SAP is investing heavily in its cloud offerings and is encouraging its customers to migrate to the cloud. SAP S/4HANA Cloud is SAP’s next-generation ERP system, built specifically for the cloud. This is a strategic move, pushing users towards a more agile and accessible platform.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being integrated into SAP ERP to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance user experience. AI-powered chatbots are being used to provide customer support, ML algorithms are being used to predict demand, and AI is being used to automate financial closing processes. The integration of AI is making SAP ERP more intelligent and efficient.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting devices and sensors to the internet, generating vast amounts of data. SAP ERP is being integrated with IoT platforms to collect and analyze this data, enabling organizations to gain new insights into their operations and to optimize their processes. For example, IoT data can be used to monitor equipment performance and to predict maintenance needs.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is being used to improve supply chain transparency and security. SAP ERP is being integrated with blockchain platforms to track goods as they move through the supply chain and to ensure the authenticity of products. Blockchain can help to prevent counterfeiting and to improve trust between trading partners.
User Experience (UX)
SAP is investing heavily in improving the user experience of its ERP system. SAP Fiori is a design system that provides a modern and intuitive user interface for SAP applications. The goal is to make SAP ERP easier to use and more accessible to all users. A better UX can lead to increased user adoption and improved productivity.
These trends are transforming SAP ERP into a more intelligent, connected, and user-friendly system. As technology continues to evolve, SAP ERP will continue to adapt and to provide organizations with the tools they need to succeed in the digital age.
Conclusion
SAP ERP is a powerful and comprehensive ERP system that can help organizations of all sizes and across various industries to improve their business processes, increase efficiency, and drive growth.
By understanding the fundamentals of ERP, the key modules of SAP ERP, the benefits of implementation, and the considerations for implementation, organizations can make informed decisions about whether to implement SAP ERP and how to successfully implement it.
The future of SAP ERP is bright, with cloud adoption, AI, IoT, blockchain, and improved UX all playing a key role in shaping its evolution. As organizations navigate the complexities of the modern business environment, SAP ERP will continue to be a valuable tool for managing and optimizing their operations.



